5 Computer Revolution from Abacus to 2024 latest Generation
The Computer Revolution
Understanding the history of computers is crucial as we delve into the various facets of computing and its history. The Analytical Engine, a universal computer created by Charles Babbage It aids in our comprehension of how technology has developed and grown over time. It is a crucial subject for competitive and banking examinations as well.
How do you define a computer?
A computer is an electrical device that gathers data, stores it, processes it in accordance with user guidelines, and then outputs the outcome.
An electrical device that can be programmed, a computer uses the user’s instructions to carry out arithmetic and logical processes automatically.
Earlier Computer Equipment
Before computers were developed, people counted using sticks, stones, and bones. Over time, as technology developed and human cognition increased, more computing devices were created. Let’s take a closer look at some of the earliest computers ever utilized by humans.
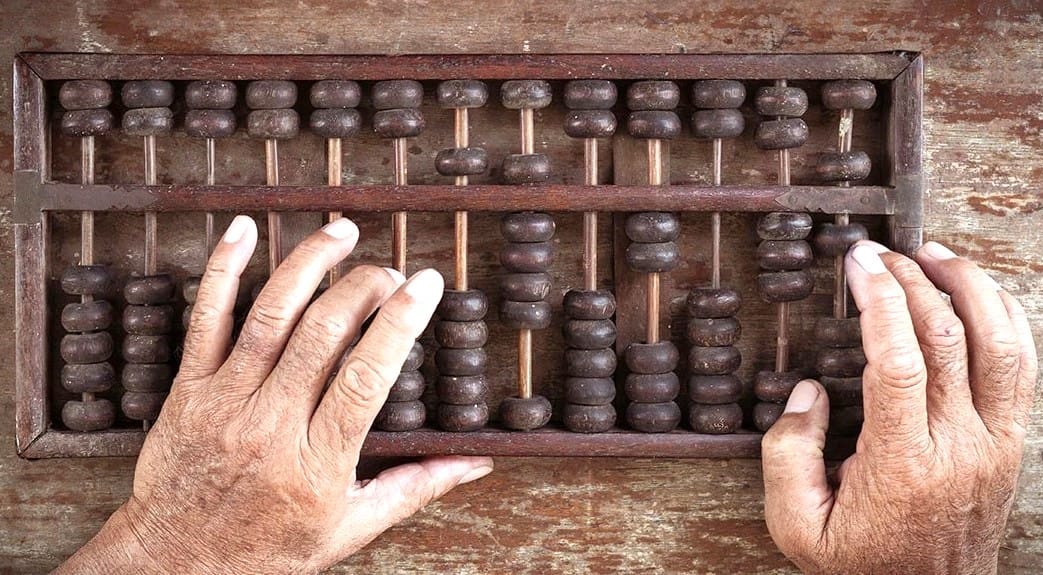
Abacus
About 4,000 years ago, the Chinese devised the abacus. The rack is made of wood, and beads are fastened to metal rods. To perform mathematical operations, the abacus operator moves the beads in accordance with predetermined patterns Computer Revolution
.
Napier’s Bone
John Napier created the manually driven calculator known as Napier’s Bones. 9 distinct ivory strips (bones) with number markings were utilized in this device’s multiplication and division calculations. Additionally Computer Revolution it was the first device to perform calculations using the decimal point system.
Pascaline
In 1642, the French mathematician and philosopher Biaise Pascal created Pascaline. Computer Revolution It is regarded as the original automated mechanical calculator. It was a wooden box with wheels and gears within.
Stepped Reckoner or Leibniz wheel
This device was developed in 1673 by Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, a German mathematician and philosopher, who built upon Pascal’s original idea. Because fluted drums were utilized in place of gears, this digital mechanical calculator was dubbed the “stepped reckoner.”
Difference Engine
Charles Babbage invented the Difference Engine in the early 1820s. It was a mechanical computer that was capable of simple calculations. It was a steam-powered calculator that was meant to solve logarithmic tables and other number tables Computer Revolution.
Analytical Engine
In 1830, Charles Babbage invented the Analytical Engine, a different type of calculator. Punch cards were the input method for this mechanical computer. It could store information in an endless memory and solve any mathematical puzzle.
Tabulating machine
This machine was created in 1890 by American statistician Herman Hollerith. Punch card-based mechanical tabulators were used in the Tabulating Machine. It could record, organize, and compute statistics as well as data and information. These devices were first produced by Hollerith’s business, Computer Revolution which in 1924 changed its name to International Business Machines (IBM).
Differential Analyzer
In 1930, Vannevar Bush unveiled the Differential Analyzer, the first electrical computer. The vacuum tubes of this machine are used to switch electrical impulses in order to do computations. In just a few minutes, it could complete 25 computations Computer Revolution.
Mark I

In 1937, Howard Aiken conceived of the idea of creating a device that could do large-scale computations or computations involving gigantic numbers. A joint project between IBM and Harvard, the Mark I Computer Revolution was built in 1944.
The Computer Generation’s History
There is a fascinating history behind the word “computer.” Those who computed, or performed computations, were the first to employ it in the sixteenth century. Until the 20th century, the term was used in the same sense as a noun. Women were employed to perform all types of computations and calculations like human computers.
The term was also applied to devices that performed computations by the late 1800s. The term is most commonly used in current use to refer to electrically powered, programmable digital devices.
Computer History in the Early Years
Devices have been used for computations for thousands of years, ever since the development of humanity. The abacus was among the most ancient and well-known tools. Then, in 1822, the inventor of computers, Charles Babbage, started working on the creation of the first mechanical computer. And he went on to create an analytical engine, a general-purpose computer, in 1833. It included the idea of integrated memory, an ALU, and some fundamental flow chart concepts.
The first general-purpose electronic computer was then obtained, more than a century later in the history of computers. The acronym for the device was ENIAC, or Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer. John W. Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert are the creators of this machine Computer Revolution.
Additionally, as technology advanced, computers became smaller and more powerful. In 1981, Adam Osborne and EPSON released the first laptops that we had.
Computer Generations
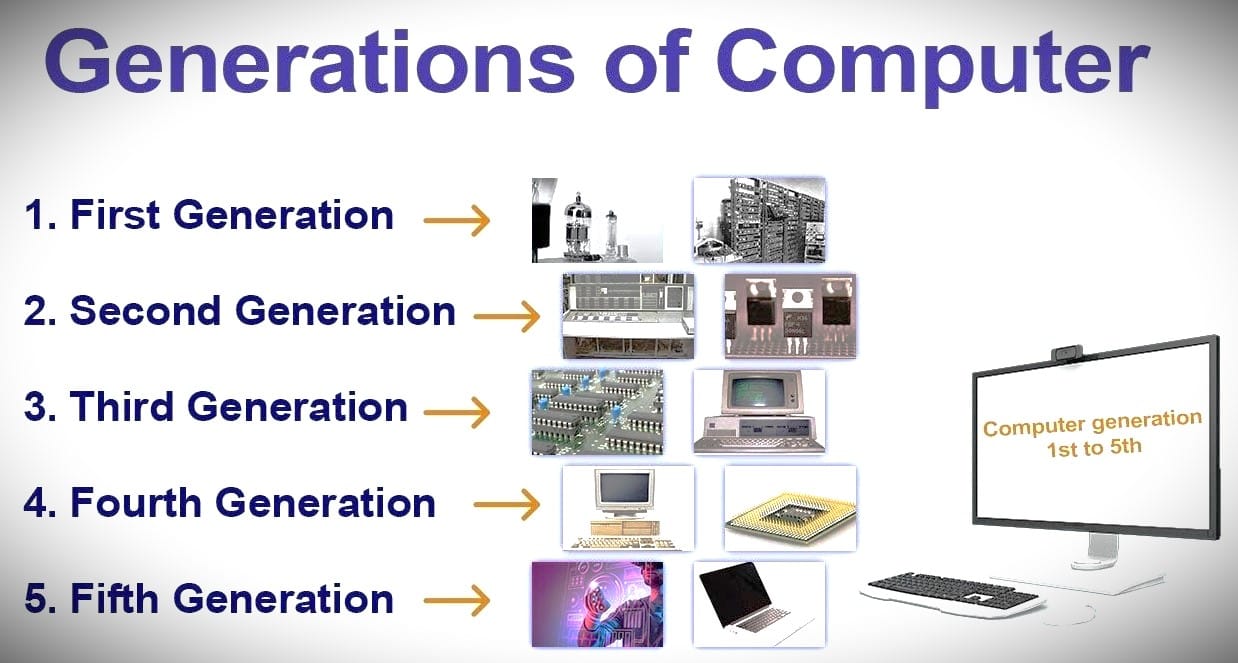
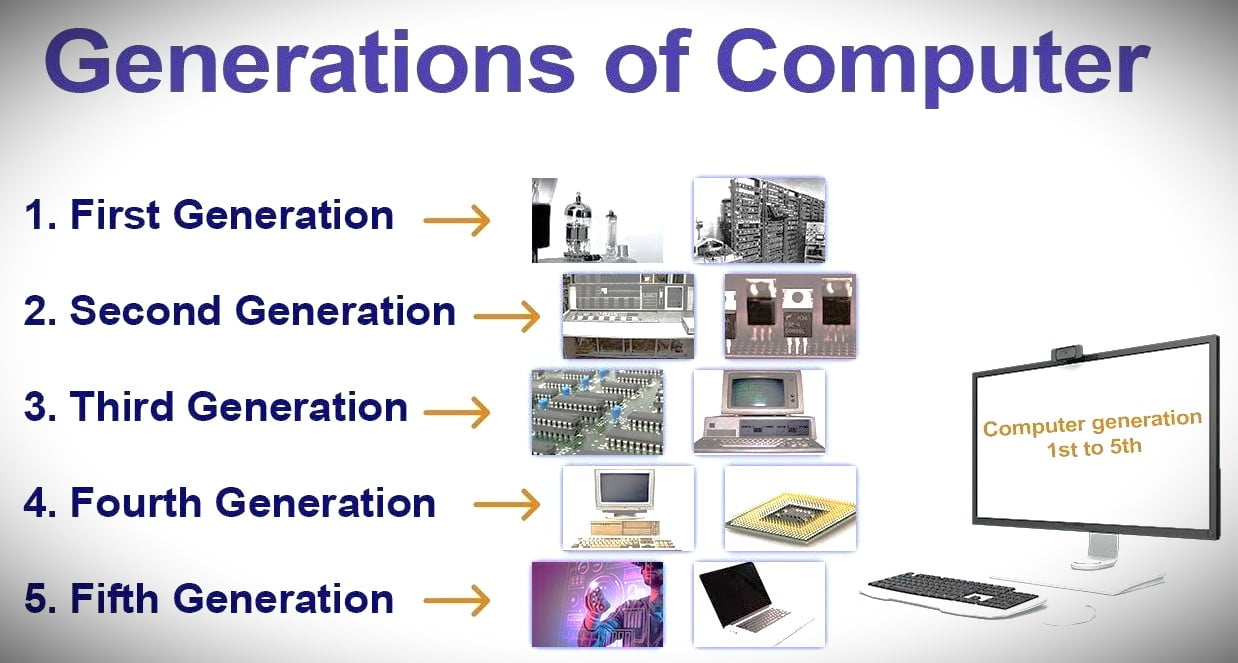
Modern computer breakthroughs are sometimes referred to as the “generation of computers” in computer history. As of right now, computers are being produced in their fifth generation. Let’s now examine the key characteristics of these five computer generations.

First Generation: They spanned the years 1940–1955. This was the period in which computer-readable machine language was created. Vacuum tubes were utilized in the circuitry. They employed magnetic drums to aid with remembering. Large, costly, and intricate, these devices were. Punch cards and batch operating systems were their main sources of dependency. Magnetic tape and paper tape were used as input/output technologies. Taking ENIAC, UNIVAC-1, EDVAC, and so forth as examples.
2nd Generation: The term “second generation of computers” was first used to describe the years 1957–1963. Programming languages and assembly languages used in second-generation computers are FORTRAN and COBOL. Here, vacuum tubes gave way to transistors. The computers became quicker, more energy-efficient, and smaller as a result. From binary to assembly languages, they progressed. As an example, consider IBM 1620, IBM 7094, CDC 1604, CDC 3600, and so on.
Third Generation: This era (1964–1971) was distinguished by the advancement of the integrated circuit. A computer’s power may be increased while also decreasing its cost since each integrated circuit (IC) is made up of several transistors. Compared to earlier models, these computers were more affordable, more dependable, smaller, and speedier. High-level programming languages including PASCAL PL/1, COBOL, and FORTRON-II to IV were used. Taking the IBM-370/168, Honeywell-6000, and IBM-360 series as examples.
Fourth Generation: The fourth generation of computers was introduced with the development of microprocessors. Computers of the fourth generation dominated the years 1971–1980. This generation of computers used the programming languages C, C++, and Java. As an example, consider the Apple II, PDP 11, CRAY-1, CRAY-X-MP, and STAR 1000. At this point, we began manufacturing computers intended for domestic usage.
How to weight loss diet Plan in Female and male, Best 5 tips
How to Gain Weight for Skinny Men and Woman, Unique 10 tips.
I can read but can’t speak fluent English. Unique 6 tips
how to grow hair faster at home naturally in a week 7 tips
how to create a blog website for free with unique 8 tips
How to Set Up Google AdSense Correctly on Your WordPress Website
6 Which jobs that AI can’t replace by AI or technology in future
Most asking 5 interview question answer for fresher jobs
Top query – computer revolution,apple computer revolution,home computer revolution,microcomputer revolution,microprocessor revolution,pc revolution,personal computer revolution,revolution computers,the pc revolution,the personal computer revolution,www revolution computer com




